Activity 8
Examine the diagram below. It shows an intertidal shore, with the tide in (upper diagram) and out (lower diagram). Note the starfish at the positions indicated by the arrows, A, B and C.
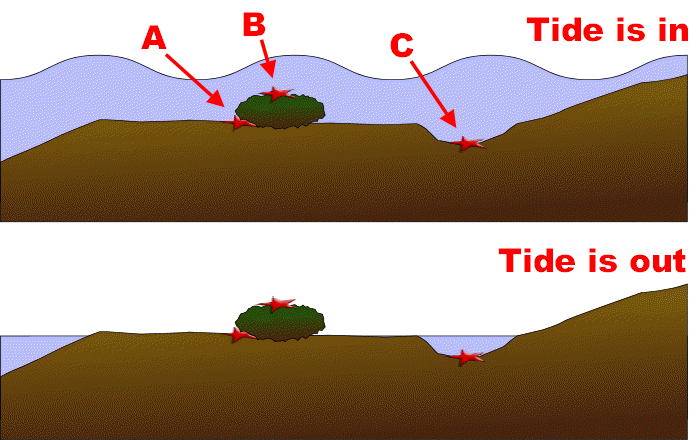
Now consider five environmental factors: light, temperature, oxygen level, salinity and physical force (from wind or waves). Assume that the shore is in a tropical region, it is a sunny day and air temperature is about 30C. Assume that the tide rises until the middle of the day, then falls.
Complete the table below to describe how conditions change for each starfish: compare a two hour period with the tide in, with a two hour period with the tide out. Three entries – oxygen for starfish A, temperature for starfish B and light for starfish C – are given as examples. When you have completed the table, go to the answer page.
| Starfish A | Starfish B | Starfish C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | The light level will be higher when the tide is out, because the water depth will be shallower | ||
| Temperature | Temperature will probably be higher, perhaps considerably higher, when the tide is out as the animal is on a dark surface, exposed to full sun; temperature may also be more variable during the period when the tide is out | ||
| Oxygen level | Oxygen level will probably be higher when the tide is out because oxygen diffuses more rapidly through air than water and the animal is initially in a position where water movement may be limited | ||
| Salinity |
|
||
| Other comments |
|