The production of ecosystem services
Ecosystem Services Derived from Ecosystem Functioning & Processing of Natural Capital
As mentioned ecosystem services are the outcome of the natural processes and functioning of ecosystems. That is, in the process of living, growing and changing, ecosystems and their biotic and abiotic components provide the essential elements needed to support and sustain human life. These biotic organisms, geological elements, water and the atmosphere, i.e. all the elements of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, are collectively referred to as natural capital.
Ecosystem services are produced by the natural processes and functioning of ecosystems that transform natural capital into goods and services useful to humans. Refer to Figure 1 for a diagrammatic representation of the production of ecosystem services and click on each of the diagram labels.
Figure 1. Ecosystem Services are produced by Transformations of Natural Capital
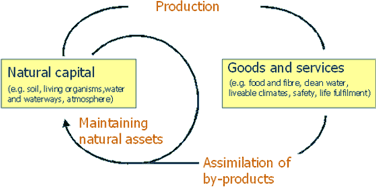
Table 3 provides a list of ecosystem services and a description of the ecosystem functions involved in their production.
Natural Capital
Natural capital is the stock of all the elements of ecosystems including biotic organisms, geological elements, water and the atmosphere and provides the raw material for life and human activities such as manufacturing, agriculture and recreation. The term natural capital is derived from the economic concept of capital and equates the natural capital of ecosystems with the highly valued capital of economic systems.
Capital is considered to be a stock of materials or information that exists at a point in time and can be used to generate, of itself, or in conjunction with services from other capital, a flow of services that benefits the well being of humans into the future (Costanza and Daly 1992; Costanza, d'Arge et al. 1998) (i.e. raw material capital + human capital + $ = manufactured product).
Natural capital is the stock from which ecosystem services flow and the processes and functions of ecosystems are the procedures or methods used to create this flow of services. Refer to Figure 1 and the imbedded information for a detailed description of this process.
The Role of Biodiversity
Biological diversity or biodiversity is an important form of natural capital and plays a vital role in the production of ecosystem services through its role in ecosystem function. Biodiversity includes both the type and composition of the genotypes, species, functional types and landscape units in a given system (Diaz and Cabido 2001). However, diversity is often equated to species richness (i.e. the number of different species), and other components of diversity have received far less attention in the literature.
A major area of ecological research involving biodiversity conservation is based on looking for possible connections between species diversity and the intensity of various ecosystem processes or functions (Ghilarvo 2000). Research in this area has focused on plant communities rather than the full array of biotic organisms. For example if we were able to identify the level of biodiversity or specific species required by an ecosystem to function sufficiently to produce the desired ESS we would be able to value and conserve the appropriate level of biodiversity.
Think about some of the problems with this approach to biodiversity conservation, e.g. lack of knowledge, the precautionary principle, preservation of options, the intrinsic value of species.
A recent review of experimental results generally indicate a positive relationship between plant species richness and ecosystem processes, especially in above ground biomass, although the types of different ecosystems studies is considerably limited (Diaz & Cabido, 2001). Another important finding of studies focusing on the role of biodiversity is the importance of functional diversity. For example Hector and colleagues found that the presence of a nitrogen fixing clover species, was of particular importance to the level of primary productivity (Hector, Joshi et al. 2001).
It is now widely accepted that one of the most important aspects of biodiversity for ecosystem functioning and the production of ESS is the functional diversity or type of species present rather than the number of species per se (Diaz & Cabido, 2001).
Identifying the species providing the essential ecosystem processes and functions leading to the provision of ecosystem services at relevant scales has been identified as a vital gap in current scientific knowledge on how ecosystems provide ecosystem services (Kremen 2005).
Interactions between Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are linked and NO SERVICE ACTS IN ISLOATION. This is largely because the same populations of species, geological elements and other components of natural capital are involved in multiple ecosystem functions and therefore a number of different ESS.
![]()
Activity 1.1
With reference to the following papers listed below and the text above, answer the following questions:
- Ecosystem Services Fact Sheet
- Ecosystem
Services: Benefits Supplied to Human Societies by Natural Ecosystems
Q1 What three reasons are given for the emphasis of natural ecosystems as the source of ecosystem services?
![]()
- Services generated by natural ecosystems are greatly undervalued by society
- Many human-initiated disruptions of ecosystems are difficult or impossible to reverse on any time scale relevant to society (i.e. need to prevent degradation and destruction because it can't be fixed or takes to long)
- If awareness is not increased and current trends continue, humanity will dramatically alter Earth's remaining natural ecosystems within a few decades.
Q2 With reference to Daily's thought exercise of colonizing the moon and the section on the character of ecosystem services what is the importance of biodiversity and what are some of the problems associated with trying to conserve biodiversity?
![]()
Your answer should include these concepts expressed in your own words;
Biodiversity is essential for the production of ecosystem services. A huge number of different species are involved in the production of any one ecosystem service and maintaining viable ecosystems. Even the production of a single food crop involves the activity of millions of organisms (for example in the soil and in providing water) and without this diversity of organisms the production of ecosystem services will be compromised.
It is impossible to select a short list of organisms that are essential for supporting human life, because although we use relatively few organisms for food, fibre, medicines etc the number of organisms required to support the production of these goods and maintain ecosystems is astronomical. In addition to we know very little or nothing about the majority of organisms (particularly soil dwelling insects and microscopic organisms) that comprise the biodiversity of natural ecosystems.
Hence the problems associated with conserving biodiversity include:
- How do we conserve so many organisms when we don't even know all the species
- There are many species yet to be discovered that could provide food, medicines, manufacturing products etc.
- We don't know all the species involved in the production of each ecosystem service
- We don't know what species are essential for the production of each ecosystem service
- If we can't conserve all species how do we select what's important to conserve
- How do we balance natures need for habitat with human needs for farmland, cities etc.
Your answer should include these points although there are many other points that could also be included.
Q3 Make a comprehensive list of ecosystem services with reference to both the information given in this section and additional resources. Define each service and briefly describe how it is produced.
![]()
Examples of possible answers include;
A major point to take from this exercise is that largely ecosystem services are produced by the interactions of living organisms, thus health functioning ecosystems require a high degree of biodiversity to ensure that there are sufficient organisms to conduct all the different processes and functions that produce ecosystem services.
Q4 Locate a diagram of the water cycle. List the ecosystem services that each component of the water cycle is involved in. For example, the atmosphere – formation of clouds from water particles, also acts as a nitrogen sink in nitrogen cycling and is involved in climate regulation etc.
![]()
You answer should at least include the following;
- Atmosphere; formation of clouds from water molecules and dust particles, N sink for nitrogen cycle, production of ozone to block UV rays, trapping infar-red radiation to produce a warm climate, etc.
- Water body such as the ocean; storage sink for water, production of goods (fish etc), climate regulation, aesthetic beauty, recreational opportunities
- Vegetation; transpiration producing water molecules in the air, filtration of water, production of goods, erosion control, genetic diversity, aesthetic beauty etc.
- Soil; Water storage and slow movement, nutrient cycling
Topics in this module
- Introduction
- What are ecosystem services?
- Types of ecosystem services
- The production of ecosystem services
- Valuation of ecosystem services
- Causes & consequences of losing ecosystem services
- Compulsory Readings




